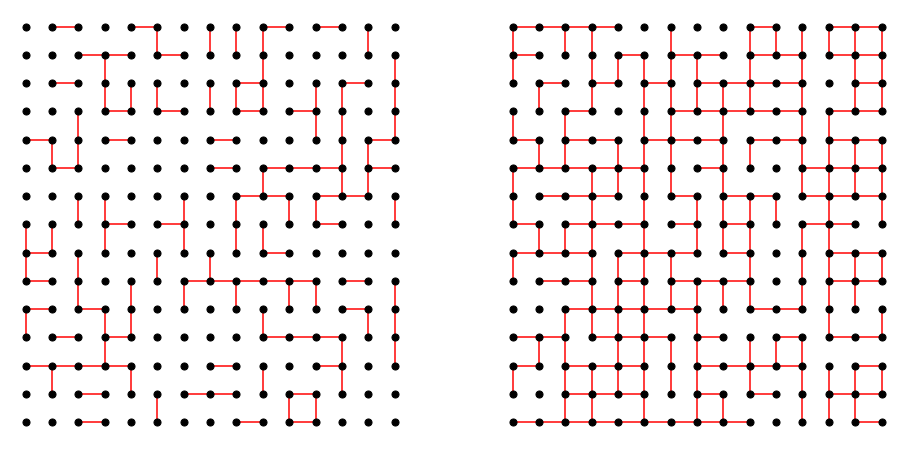Critical Phenomena
Contents
Critical Phenomena#
There exists a critical value \(p_{\mathrm{c}}\) of \(p\) such that
\[\begin{split}
\theta(p)\begin{cases}
=0, & p<p_{\mathrm{c}}\\
>0, & p>p_{\mathrm{c}}
\end{cases}
\end{split}\]
\(p_{\mathrm{c}}\) is called the critical probability defined as
\[
p_{\mathrm{c}}=\sup\{p\mid\theta(p)=0\}
\]
List of known critical probabilities \(p_{\mathrm{c}}\)#
Lattice structure |
critical probability \(p_{\mathrm{c}}\) |
|---|---|
Square lattice |
\(p_{\mathrm{c}}=1/2\) |
Triangular lattice |
\(p_{\mathrm{c}}=2\sin(\pi/18)=0.34729\dots\) |
Hexagonal lattice |
\(p_{\mathrm{c}}=1-2\sin(\pi/18)=0.65270\dots\) |
bow-tie lattice |
\(p_{\mathrm{c}}=p_{c}(\textrm{bow tie})=0.40451\dots\) |
Note
\(p_{c}(\textrm{bow tie})\) is the unique solution of the following polynomial in the interval \((0,1)\):
\[
1-p-6p^{2}+6p^{3}-p^{5}=0
\]